Hello Interactors,
It’s been awhile. I’ve been off getting our kids settled at college…including a transfer to Los Angeles. And I may have also been seduced by the lazy days of summer.
After dropping our son in LA, my wife and I took some time to return to Santa Barbara where we first met. I was reminded of how uniquely beautiful that place is. It’s also host to a unique collection of physical geography. And while it mostly enjoys a cool, calm environment, it can also endure bouts of destruction and renewal. A bit like all of us.
Let’s reflect, shall we…
MIGRATIONS, MOUNTAINS, AND MEMORIES
Traversing the globe dropping offspring is as old as humanity. As far as we know, early hominins like Homo erectus first stepped out of Africa two million years ago. The oldest human skeletal remains outside of Africa to date were found in Eurasia (now the country of Georgia) and are 1.8 million years old. These waves of migrations were likely driven by changes in climate, resources, societies, and technologies — the same factors driving migration today.
Our oldest kin dispersed widely across Eurasia, reaching as far as Southeast Asia. Some may have even used primitive boats to navigate to and between islands. This all set the stage for later migrations of other hominins, including Homo sapiens, as they spread across globe over the next million years.
I was reflecting on this on a hike my wife and I recently took in the foothills of Santa Barbara (where we had our first date 34 years ago!). The Santa Ynez Mountains were uplifted during the late Miocene (23.03 million years ago) to early Pliocene (2.58 million years ago) due to the tectonic interactions between the Pacific and North American plates. This exposed a complex layering of ancient marine and terrestrial sediments that were deposited over millions of years in a marine basin stretching from current day central valley of California to Northern Mexico.
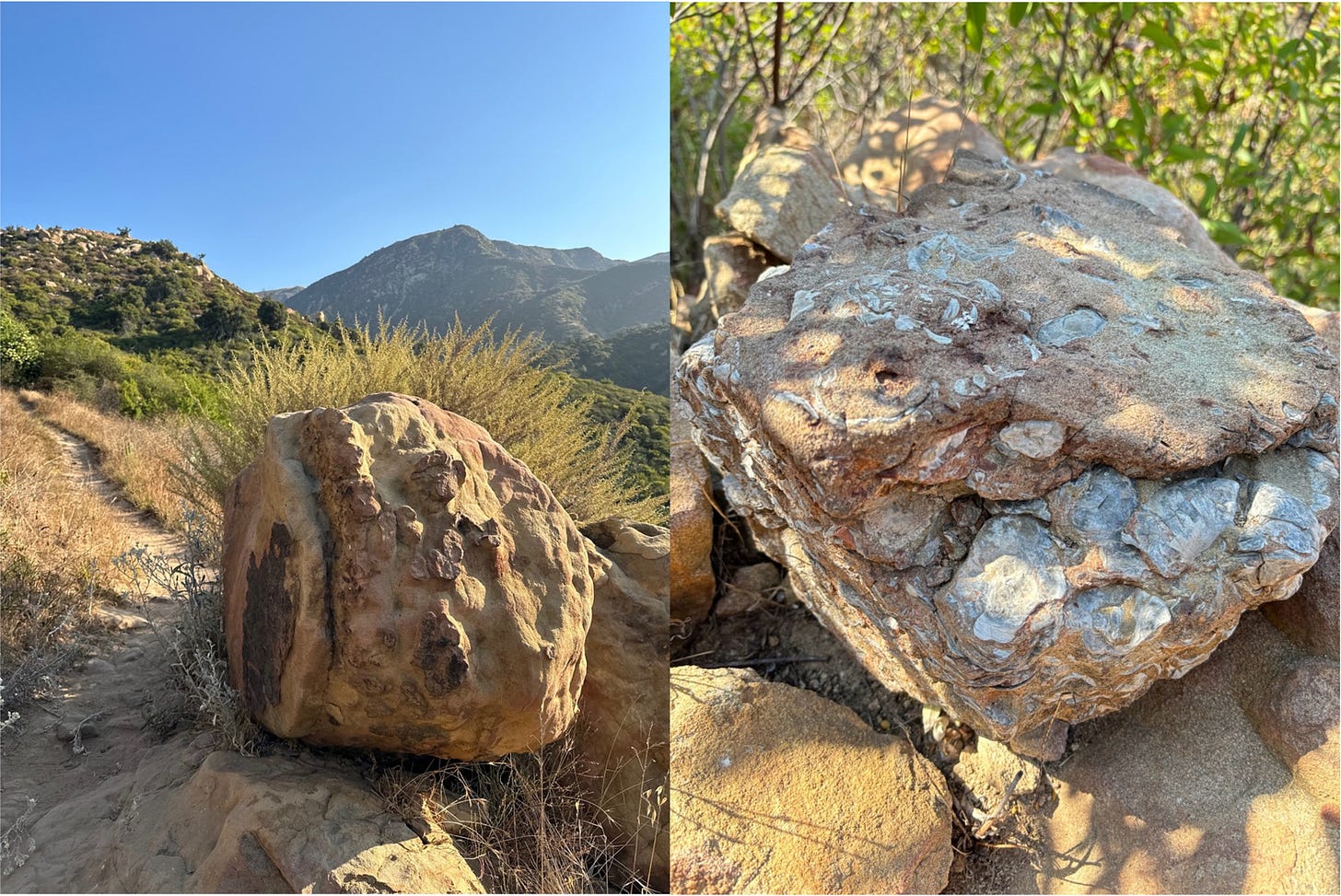

These sandstones, shale, and conglomerates are revealed along the trails, cliffs, ridges, and valleys we traversed, all formed by folding, faulting, and fanning of eroded debris. The mountains continue to be pushed upward at a rate of 1 to 4 millimeters per year due to the ongoing compression between the tectonic plates along the dynamic San Andreas Fault — the same fault that originally formed them millions of years ago.
The Miocene epoch, with its warmer and more humid climate, supported dense forests of subtropical and temperate species in the Santa Ynez Mountains. As tectonic activity uplifted the region, new habitats emerged, setting the stage for diverse vegetation to develop. This period laid the groundwork for the ecosystems that would later evolve as the landscape continued to change.
By the Pliocene, global cooling led to drier conditions, favoring the transition from these lush forests to the more arid-adapted plant communities found today. The chaparral, oak woodlands, and coastal sage scrub we hiked through are products of this shift. These plants adapted to the region's famous Mediterranean climate, characterized by hot, dry summers and mild, wet winters, and further shaped by the ongoing geological forces at work in the area.
The resultant Santa Ynez Mountains significantly influence the weather patterns in Santa Barbara by acting as a barrier to the Pacific Ocean's marine air. Unlike much of the California coast, the Santa Barbara area faces south. During the summer, these south facing mountains trap the marine layer — a cool, moist air mass that forms over the ocean—leading to fog and low clouds along the coast. This marine layer helps keep temperatures in Santa Barbara cooler than in areas further inland, providing a mild and comfortable summer climate. Additionally, in winter, the mountains enhance orographic lift, causing moist air blown from the south to rise, cool, and condense, resulting in increased rainfall on the windward side of the range and benefiting the coastal regions. I recall one brisk winter morning in Santa Barbara in 1990 when frost appeared in the shadows on the roads and snow dusted the peaks of the Santa Ynez mountains.

However, these mountains also create a rain shadow effect on their leeward side, where descending air becomes warmer and drier, leading to less precipitation. This topographical influence also contributes to the occurrence of sundowner winds—warm, dry winds that descend from the mountains into Santa Barbara. These winds can cause rapid temperature increases and lower humidity levels, sometimes creating critical fire weather conditions. My wife, then girlfriend, and I ran a 5k in 1991 that was overcome with smoke from fire stoked by these sundowner winds.
BLAZE, BURST, AND BLOOM
Similar winds, Santa Ana winds, stoked a more and recent severe fire, the Thomas Fire, in 2017. These winds form east of the Sierra Nevada mountains over inland deserts and west towards the coast. Hot and dry winds channel through mountain passes and canyons, gaining speed as they descend across Southern California — and they can amplify even the smallest fire. The Thomas Fire was one of the largest wildfires in California history burning over 280,000 acres of wildlife and more than 1,000 buildings. Firefighters in Montecito, the northern-most destination, battled for days to save homes and lives.
This left big chunks of the Montecito foothills charred. As crews worked to clear debris over the next month, the area was hit with a torrent of rain. While rainfall in Montecito was relatively minimal on the morning of January 9th, 2018, rainfall further up the mountain, enhanced by the mountain’s orographic lift, was more severe. Residents were caught off guard as waves of water gained speed through canyons and creeks picking up charred debris and uprooting trees loosened by saturated soil.
These post-fire debris flows, which included mud, rocks, and tree branches, reached heights of up to 15 feet speeding an estimated 20 miles per hour. The disaster resulted in 21 fatalities, two missing persons, and about 163 people hospitalized. Property damage exceeding $177 million, emergency response hit at least $7 million, and another $43 million was slated for cleanup and restoration.
Six years later, hiking in these same hills, we saw evidence of county crews still restoring and re-shoring the foothills. We also saw evidence of plants re-emerging. Some of which are descendants of the same ancient plants that emerged in the Pliocene in the very same soil we were walking on.
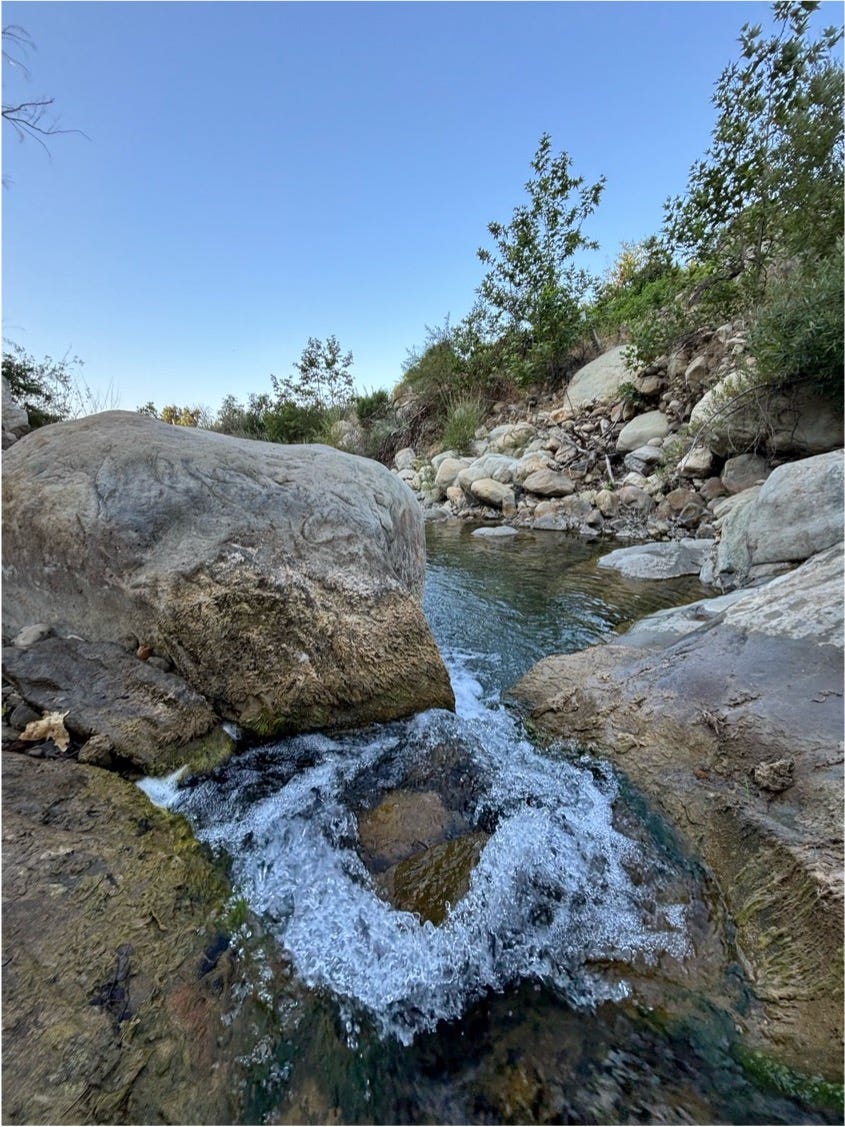

Hiking, and sometimes running, through the recovering foothills of Montecito, I was struck by how much this landscape mirrors a story of resilience that extends far beyond these hills and long before our time there. Over the previous two weeks my wife and I had crisscrossed the USA, east to NYC and west to LA, dropping our kids far away — modern migration with echoes of long ago, still alive still today.

Like other humans that moved across vast distances, we and our kids are adapting to new environments and new stages in life. Just like the chaparral and black sage of these foothills.
The plants that now re-emerge from the scorched and scarred earth are descendants of those that first appeared in the Pliocene. They use fire to propagate and regenerate in challenging terrain. Chaparral species, like black sage, evolved to thrive in this fire-prone environment. Fire-stimulated germination allows seeds to lye dormant until they’re exposed to heat which triggers germination. Sprouts emerge from underground lignotubers, which are complex energy-storing structures that quickly regenerate new shoots — even amidst scorched soil. Serotiny, another adaptation, turns seed cones into popcorn like capsules that only open when exposed to fire's heat giving them a head start on invasive competition. These strategies enable chaparral plants to not only survive but to capitalize on the aftermath of wildfires and hillside scraping floods.
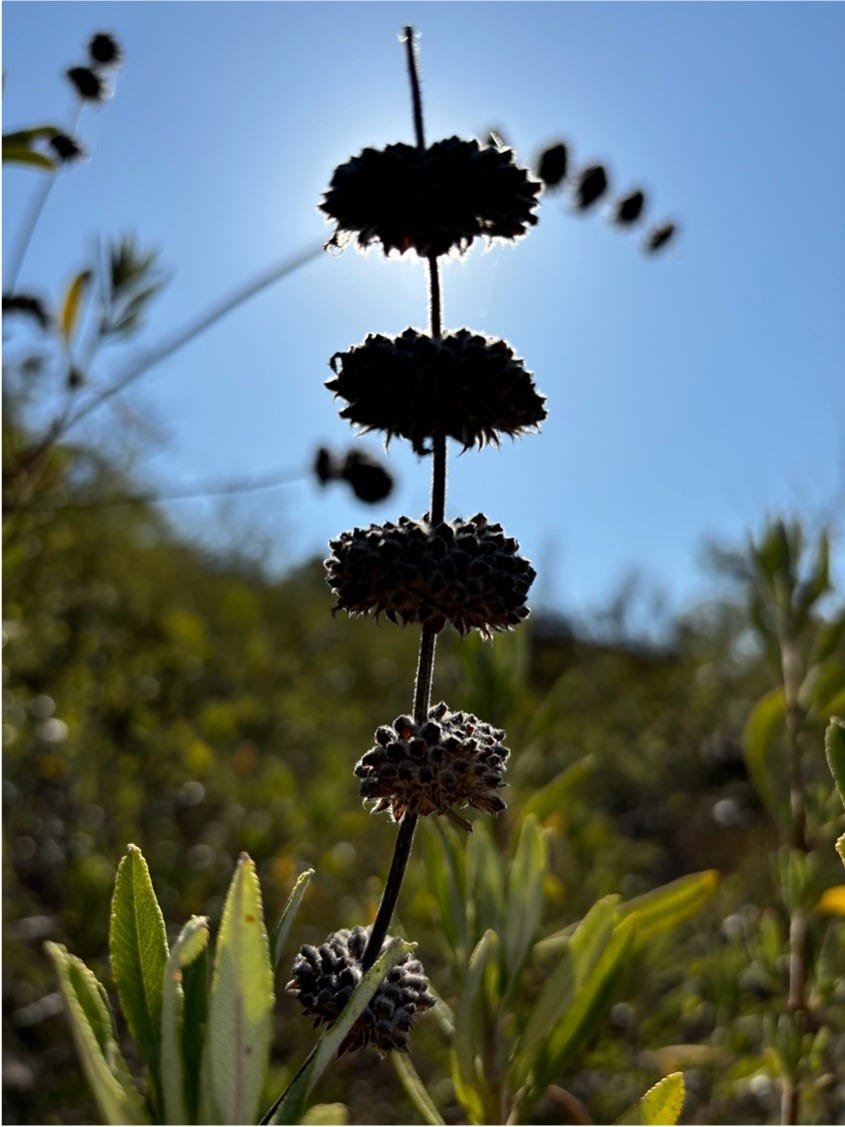

In the charred and healing soil beneath our feet, I saw the enduring connection between past and present, nature and nurture — a reminder that our journeys, like those of the landscapes we inhabit, are shaped by the unyielding push and pull of time — of adaptation, and resilience. Just as the chaparral plants of the Santa Barbara foothills have evolved mechanisms to thrive after fire, our kids, too, will develop new strategies to adapt and flourish in their new environments. In the face of life's inevitable challenges, they will learn to not only survive but to rise stronger, just as the ancient mountains of Santa Barbara continue to do. All the while, the landscapes beneath our feet continue their unbroken cycle of destruction, renewal, and growth amidst ever evolving climates, resources, societies, and technologies.