Hello Interactors,
I’m back from planting our kids at college. Now we watch our not-so-little Weed’s grow from a distance. I had a recent visit from a plant scientist friend last week that inspired me to dig into the blending of traditional Western science and Indigenous knowledge. Each have a lot to offer human adaptation strategies to the effects of climate change, but to do so will require new approaches and increased sensitivities to generations of abuse, neglect, and disrespect. This is part one of a two-part series that starts with a grounding in what integration exists today and why it’s important.
As interactors, you’re special individuals self-selected to be a part of an evolutionary journey. You’re also members of an attentive community so I welcome your participation.
Please leave your comments below or email me directly.
Now let’s go…
TEARS OF JOY AND SORROW
It was cause for celebration, but hers were not tears of joy. It was the ten-year anniversary of the largest dam removal in United States history. The Elwha Dam was completed in 1921 to dam the 45-mile-long Elwha River for electricity generation under the settler colonial banner of “Power and Progress.” A second larger dam was built in 1927. The Elwha is the fourth largest river on the Olympic Peninsula that sits on the western most Pacific coast of Washington State. It was once home to the country’s second largest salmon run behind Alaska. After the dams were built, they robbed these fish of 40 miles of habitat.
They also robbed the Lower Elwha Klallam Tribe - ʔéʔɬx̣ʷaʔ nəxʷsƛ̕áy̕əm̕ – “The Strong People” of their food source and economy while submerging their spiritual land and identity in 21 million cubic yards of sediment. That’s over one million dumpsters full of rocks and sand. If you stacked them, they’d reach over 700 miles into the air. Placed end to end they’d stretch over 3000 miles across America coast to coast.
And now, ten years later, the salmon are running again, habitat is getting restored, and the sediment is redistributing. So why the tears? For scientists to accurately measure the successes of dam removal – and further justify the removal of more dams worldwide – the federal, state, and tribal governments agreed to a moratorium on fishing the returning salmon. It seemed a worthwhile compromise to the tribal community, but after over one hundred years of suffering their losses – and seeing the fish run as their elders had once seen – their yearning for a return to their cultural heritage has intensified over the last decade. Recent years of healthy salmon runs have tested their patience with colonial powers continuing to dictate their way of life – even as they simultaneously celebrate their joint successes.
It was the U.S. Congress who passed the Elwha River Ecosystem and Fisheries Restoration Act in 1992 to restore dwindling salmon populations, but it was the Lower Elwha Klallam Tribe who had fought to have those dams removed even as they were being built. They also helped fund the research necessary for successful removal. And now they want to live as they once did – in a self-determined and self-sustaining autonomous but integrated coexistence with their neighbors.
A friend of mine1 is a plant scientist for the project who attended the celebration event in Port Angeles, Washington last week. The early economic growth of this city depended on the electricity generated by those dams. He told me the words and subsequent tears by the woman representing the tribe was the most gripping and poignant moment of the event. It left many scientists conflicted about the proper path forward.
Continued research will help with planning of future dam removal projects, including what would displace the Elwha project as the largest dam removal effort in history on the Klamath River.2 This project involves the removal of four dams that stretch across the Oregon and California border.
But what is more important? More data collection and academic papers supporting future dam removals or resuming the human rights of an abused and afflicted Klallam community? The answer won’t come from the scientists, but from deliberations between multiple levels of governments, agencies, and departments strewn across many jurisdictions.
BRIDGING BARRIERS
The Elwha dams are representative of countless ecological discontinuities brought on by colonial expansion and attempted erasure and conversion of Indigenous cultures and populations around the world. The Elwha dam removal indeed created a precedent that inspired ecological restoration projects worldwide. And while the collaboration between members of the Klallam people and U.S. government officials, volunteers, and scientists has largely been healthy, the tension that spawned the removal in the first place still remains – competition for fishing rights.
These dams posed an immediate threat to the Klallam people and their way of living, as they still do for the Klamath people and others like them. But a greater compounding threat grows more imminent every day – the effects of climate change. Despite minimal contributions to causes of climate change, Indigenous populations suffer the greatest risks of the effects. This is most apparent and acute right now in Pakistan as one third of that country remains flooded.
Pakistanis are indeed in need of outside help. But too often Western aid swoops in with relief and then disappears leaving them with little support for how to survive the next disaster. Just as profit seeking colonists left the Klallam people with little support for survival. But instead of resorting to fatalistic language and traditional paternalistic hero mentalities that portray Indigenous communities as helpless and hopeless, some scientists and activists are shifting toward community-based adaptation strategies. These efforts start by first experiencing and understanding how these communities are affected, but then recognizing many of them also have deep ancestral knowledge and history of how to adapt to a changing climate.
To strike a healthy balance between Western government aid and scientific knowledge and local needs and culture will require increased sensitivities to historical traumas inflicted by colonization, extreme capitalism, and forced acculturation. There is a myriad of language, linguistic, and cultural gaps that challenge the documentation, translation, and integration of Western scientific approaches with Indigenous ecological and cultural knowledge so that it is accurate, complete, and fair. Meanwhile, the planet is warming, the environment is shifting, and the pressure for adaptation systems and mechanisms is mounting.
To bridge these knowledge gaps requires a concerted effort around the globe to establish consistent approaches to Indigenous knowledge integration in scientific literature. In 2020 a group of researchers started by asking this fundamental question:
“How is evidence of indigenous knowledge on climate change adaptation geographically and thematically distributed in the peer-reviewed literature?”3
What they found is the number of publications per year focusing on Indigenous knowledge and climate change adaptation has grown considerably over the last ten or so years. Between 1994 and 2008 their search yielded just six scientific publications that included evidence of Indigenous knowledge. There were that many in 2009 alone. Ten years later, in 2019, the number grew sevenfold to 42.

The majority, 133 of the 236 sampled, came from the field of Environmental Science. Social Sciences (97) and Earth and Planetary Sciences (50) had the second and third most publications respectively. Then came Agriculture and Biological Sciences (36), Medicine (22), and Health Professions (14). The word-cloud they generated from the corpus ranked these as the most common words: ‘vulnerability’, ‘resilience’, ‘drought’, ‘community’, ‘perception’, ‘impact’, ‘food security’, ‘agriculture’, and ‘adaptive capacity’. Given the most repeated words all relate to health and survival, researchers in the health and human services academy and industry have some work to do.
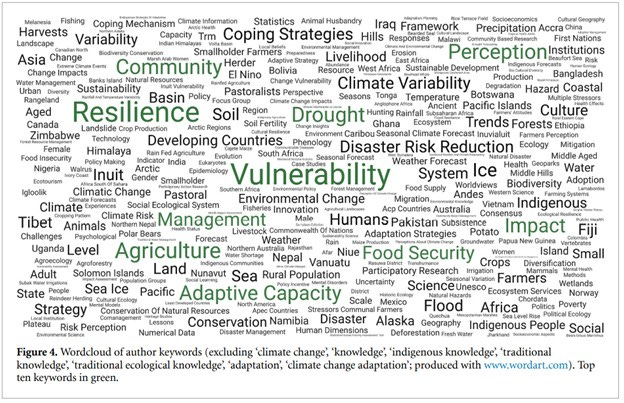
In terms of geographic distribution, a large proportion of publications study regions in Africa and Asia. The most studied countries are India, Zimbabwe, and Canada. There is no worldwide count of Indigenous populations and most studies don’t mention tribal names, so it’s hard to determine fair distribution. However, based on the data available, the authors suggest the biggest gaps may be in central Africa, northern Asia, Greenland, Australia, parts of South America and Polynesia.
Of the attributes of Indigenous knowledge represented, most publications (170) included “Factual knowledge about the environment and environmental changes” like precipitation, temperature, ice thickness, and wind speed. Two of the least represented attributes were:
“Cultural values and worldviews (61) like relationship to land, stewardship, values of reciprocity, collectiveness, equilibrium, and solidarity.
“Governance and social capital” (61) like food sharing and social networks as well as informal social safety nets.
These seem to me to be valuable sets of knowledge in the face of worldwide human ‘vulnerability’, ‘resilience’, and ‘capacity to adapt’ to the effects of climate change. Some scientists are shifting from describing the facts of climate change toward better understanding of human mitigation, migration, and adaptation.
BLENDING BARRIERS
One of the reasons Indigenous communities are so helpful is their cultural lineage and oral history traditions include solutions, strategies, and innovations of past human adaptations to a changing climate. This all despite past attempts by evil colonizers to suppress and destroy their knowledge, traditions, and even their existence. But these people and civilizations gained and sustained through generations of ecological experimentation. They benefited from innovations in grassland growth, fire management, and crop alteration.
Over decades and centuries, they evolved countless trials of seed germination, hybridization, and dispersal to achieve maximal crop yields. (e.g., symbiotic ‘Three Sisters’ crop clustering). They also developed predator management schemes enabling them, and their crops, to survive and thrive. Their mediation of the environment provided a mutualistic food web rooted in natural forms of ecological reciprocity. But this knowledge was not and is not static.
They had to endure and adapt to environmental dynamism at varying scales of time and space. Change occurred at a local level with daily shifts in the weather but also at a regional level from sudden climatic and geological perturbations like earthquakes, floods, droughts, and volcanoes. All of which had effects lasting decades and centuries.
These events led some populations to hunker down and innovate new methods of survival amidst a changed but familiar environment, while others migrated near and far to survive. For those who didn’t make it, their knowledge is lost. However, some traces of their existence, their paths of migration, shelter, and food habits do, and we rely on archeologists to bring those facts and interpretations to light.
But even in the best of situations, as evidenced with the Elwha project, balancing hard quantitative science with qualitative humanitarianism while in search of adaptation and survival strategies poses a host of challenges. Not the least of which is the fact that within these works exist many gaps in human and environmental knowledge across the spectrum of global space and time.
But a new approach in archaeology and ecology is emerging called ‘archaeoecology. It strives for a more robust intellectual understanding of the interaction of people and place that spans the globe and the past 60,000 years of existence. It’s a proposed blending of ecological and archaeological research that, when augmented with Traditional Ecological Knowledge, can fill gaps of the past so that plans can be made now for how humans can survive in the future. And as the Klallam people have reminded us, regardless of the past, the time for healthy adaptation to a changed environment needs to start now.
I mention my friend, Pat Shafroth, in this piece from last year: Big Science Meets Big Ecology under the Big Sky – How one man launched a quantitative approach to systems ecology in just a few short years.
Klamath was in the news last summer with severe drought conditions. I wrote this piece on elements of the area’s Indigenous history and environment. Calamity in Klamath – Mukluks suffer over water for suckers.
Indigenous knowledge on climate change adaptation: a global evidence map of academic literature. Jan Petzold, Nadine Andrews, James D Ford, Christopher Hedemann and Julio C Postigo. Environmental Research Letters. 2020.