Hello Interactors,
The Olympics are in full swing. I admit I’m staying up later than I probably should be, but I’m a sucker for the Olympics. Yes it’s strange seeing a white strip of snow down a brown windy hill or watching big air competitions against a dystopian industrial waste site, but hey, that’s Beijing! But maybe I’m being too judgmental. Surely there’s more than meets the eye.
As interactors, you’re special individuals self-selected to be a part of an evolutionary journey. You’re also members of an attentive community so I welcome your participation.
Please leave your comments below or email me directly.
Now let’s go…
THE GU GLUE
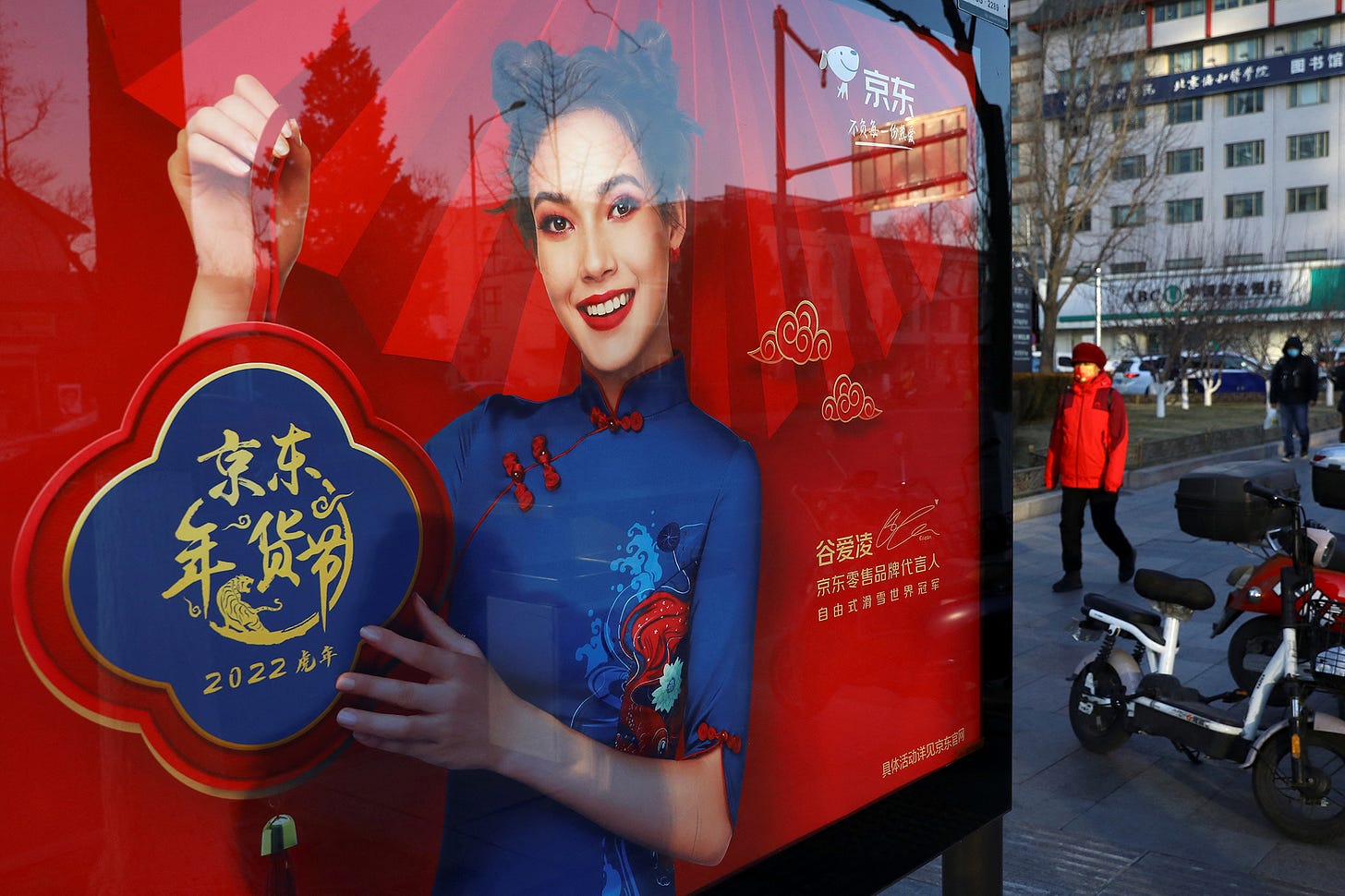
Jubilant in her successful landing, the Chinese skier put on the brakes spraying snow over the blue padded barriers as the camera centered her in the frame. She had just landed her first jump in the Olympics’ big air competition. She pulled off her goggles and beamed a big, immaculate toothy smile into the camera. My first thought was, “This girl is not Chinese.” I had never heard of Eileen Gu, but that was about to change.
She had just landed a right double 1440. That’s four full gravity defying rotations in the air after descending a hill 20 stories high and then launching off a curved ramp pointed to the sky. She was the first woman to land a similar double cork 1440 just two months prior. That prompted the French skier, Tess Ledeux, to counter in January by being the first woman to land a 1620 – four and a half rotations.

Ledeux managed to land that same jump in her opening run at the Olympics in Beijing earlier this week and held the top spot until Gu’s third and final jump. While Gu was at the top waiting her turn, her mom called from the stands at the bottom of the hill. Yan Gu introduced Eileen to skiing in Lake Tahoe where she sometimes worked as a ski instructor. She told her daughter to play it safe and stick to the 1440. Eileen responded,
“Mom, executive call here, vetoed. I am going to make the 16, and you are going to deal with it.”
After visualizing the trick when her eyes closed, arms swaying, shoulders jerking, like a dog running in their sleep, she aimed her skis down the slope. High in the sky, confident in her 1620 launch, Gu grabbed the bottom of her ski – a safety grab – a trick she had never attempted before this run. She landed triumphantly and the judges launched her into first place. As she threw her fist in the air in celebration it was rewarded with a loud cheer from the Chinese fans sprinkled throughout the stadium. Her mom, of course, being one of them.
Yan Gu was born in Shanghai and grew up in Beijing. The Olympics are in her home town. Her mom, Eileen’s grandmother, still lives there. When Yan was in her twenties, she did what many other Chinese students did, and continue to do. She sought an education in America. After receiving a degree in chemistry from Peking University in Beijing, she enrolled in a master’s program in biochemistry and molecular biology at Auburn University in the late 80s. She went on to be a research associate at Rockefeller University before going on to earn an MBA at Stanford in 1994. She now works at an investment firm in San Francisco where she specializes in Chinese investments.
The director of an extreme outdoor sports high school in Mt. Hood Oregon, Mike Hanley, said “Yan is very pleasant but one of the most intense human beings I have ever met in my life. She smiles and tells you how great you are. But then you find out, after the fact, what the requests are. She loves her daughter and wants her daughter to get priority.”

Getting priority attention from coaches and trainers in America means paying more money. Extorsion? Maybe. But money talks. Yan, a single parent, was willing to pay whatever it took to secure the right training to match her daughter’s ability and her own drive to insure her child’s success. Not many parents of talented kids can afford to do this without striking deals with big name extreme sports brands, like Red Bull or Burton, on behalf of their kids. Child labor? Maybe. But it pays the bills.
But Yan has been off the hook for paying much at all since her daughter started striking her own lucrative modelling and endorsement contracts. She’s was a millionaire before hitting 18. She not only landed Red Bull, but Cadillac, Apple’s Beats by Dre headphones, Tiffany’s, Louis Vuitton and Victoria’s Secret. Those are some big names. But in China she’s also paid to represent the Bank of China, China Mobile, a milk company, and Starbucks of China. She is estimated to command $2.5 million per deal. With over 20 modelling, spokesperson, and endorsement deals she must be worth over $50 million dollars at age 18. And that was before she won the gold medal.
In addition to being beautiful, talented, and rich, she is also smart. She scored 1580 on the SAT out of a perfect score of 1600, was the first to graduate early at her private high school in the Bay area, and will attend Stanford next fall. Oh, and did I mention she plays the piano and was one of the top distance runners in the state of California before turning her attention to the Olympics? She is what overly competitive parents the world over wish their kids to be. Sorry kids of demanding parents, Eileen has set the bar high. And for Eileen, good luck living through the onslaught of Western chauvinism, racism, and ethnocentrism. Not to mention a healthy dose of wealth, ability, and beauty resentment and jealousy.

Gu decided, supposedly with her mother’s urging, to compete for China three years ago when she turned 15. She had grown up fluidly splitting her time between China and Chinese language and culture and the U.S. and American culture. As she said in a press conference this week,
“in the US, I’m American, and when I’m in China, I’m Chinese”.
But reporters, mostly male, weren’t satisfied with the answer. The English sports reporter, Oliver Brown, thought that line was “a cute line, but sadly impractical, for the simple reason that China does not recognise dual citizenship.” Gu refuses to indulge reporters on admitting whether or not she renounced her U.S. citizenship or whether the Chinese government made an exception for the girl the Chinese media call “Snow Princess”. Insistence by Western media, and many others, on making a bi-racial teenage woman pick one side or the other will likely not relent any time soon.
REPRESENTATION ORIENTATION
I’m reflecting on my own initial reaction to learning Gu wasn’t representing America. My first thought, like many, is she’s a product of American culture, education, coaching, and lavish ski schools and resorts. Other athletes are saying the same thing. Jen Haduk, a Winter X Games gold medalist and a former member of the U.S.A Women’s team, told the New York Post that
“[Eileen Gu] became the athlete she is because she grew up in the United States, where she had access to premier training grounds and coaching that, as a female, she might not have had in China…I think she would be a different skier if she grew up in China. This makes me sad.”
Eileen Gu admits the access she had to snow, coaching, and opportunity allowed her to pursue her dreams and potential. In an interview on NBC, they show her giving a speech in middle school on the impact Title Nine had on women and sport. She also reveals in that interview that every trick she learned in America she took to China where throngs of young Chinese girls were eager to learn from her.

A Chinese-American girl fluent in Mandarin teaching Chinese girls to do tricks on skis also helped her become the athlete she is. Eileen Gu would not have been the skier she is had she grown up in China, but Chinese girls will now grow up trying to become the skier she is. And you can bet the Chinese government will see to it they have what they need to succeed. In fact, some believe it was the money and support China offered Eileen Gu three years ago that may have contributed to her decision to represent that country. An offer the American team I’m sure could not match. Another Yan Gu deal made on behalf of her daughter? Perhaps. But you can bet other parents of bi-racial or dual citizenship kids would be tempted to do the same.
Eileen Gu was born with rare athletic abilities. She was also born fearless. It was one of the reasons her mother made sure she had ski lessons. She could see as a young child that her daughter lacked the kind of fear most of us have skiing fast down a mountain of snow and ice. After suffering a concussion as a young teenager on a practice run, an injury that put her out of commission for a week, she couldn’t wait to get back to jumping. These natural abilities cannot be taught regardless of where you grow up.
And we shouldn’t be so quick to diminish Eileen’s lived experience as a Chinese-American routinely visiting her family in China. While it has only accounted for five or six years of the 18 she’s been alive, it’s undeniably part of who she is, what she does, how she thinks, and what she believes. But I, like so many others, didn’t consider that in my initial reaction and judgement of Eileen Gu. I jumped to seeing her as representing a country and only after did I question my reaction and come to see her as a human being.
As geographers Alan Latham and David Conradson wrote in 2003, even the field of human geography is “Dominated by an obsession with the politics of representation.” Little interest has historically been given to “considerations of the place, or the productiveness, of practice” by individual human beings.1
By seeing Eileen Gu as Chinese-American, bi-racial, or dual citizen can lead to objectification and categorization. There is a growing understanding and recognition in the social sciences that race categories often lead to either feelings of fear or desire. For example, unkept asylum seekers crossing the border from Latin America may elicit fear leading many to want to kick them out. Meanwhile, a super-model, Chinese-American, Olympic gold medal athlete elicits a desire to claim her as ‘theirs’.
As we sit and watch Eileen Gu smile for the camera after performing death defying feats with sublime grace or see a magazine cover graced with her face, we are reduced to dwelling on her race. Those of us in the West have grown up being barraged with pictures, paintings, movies, comics, and text that portrays races different from our own in insufficient and often inaccurate ways.
For China and the Chinese it’s a form of Orientalism. The word Orient is derived from a Latin word oriēns which can mean anything originating from the East, including the sky, sun, or lands and people East of Europe. Orient was thought of as the East and it’s antonym, Occident, was thought of as the West.

This word and it’s denotations and connotations allowed Western scholars, writers, artists, and designers to divide the world between ‘us’, the West, and ‘them’ the East. The Orient was portrayed as a place far away with exotic customs, cultures, and people – ‘Other-than’ or ‘Other-worldly’; a place to be explored, conquered, and diminished. Consequently, its people were portrayed as ‘Others’ who were to be either ‘saved’, slaved, exploited, or killed. It’s a portrayal that continues to this day.
James Bond is the suave savior from the West who is shaken by exotic foreigners but stirred to action through acts of either violence or sex. And while we know it’s fiction, it’s filmed in a pseudo-authentic way that often includes a wink or a nod from Bond into the camera. Indiana Jones does the same thing. Steven Spielberg told it’s creator, George Lucas, it’s a “James Bond film without the hardware.”
MIND AND BODY EQUALITY
The late Jamaican-British sociologist, Stuart Hall led efforts beginning in the 1960s to include race and gender in the scholarship of cultural studies. He observed in 1993 that social scientists, including post-colonial geographers, continue to downplay the role text, images, and symbols play in how we relate to the representation of cultures foreign to Western tradition. He believed representation should be considered within a wider cultural context. Hall believed the
“processes of artistic production and ownership, use of media technologies, practices of distribution, government legislation and regulation, as well as different forms of audience consumption across the globe, influence how an image is ‘read’ and understood.”2
For highly produced imagery like Bond films or pictures of Eileen Gu in an advertisement, there is an intent by the producer of the image to encode a particular message to the viewer. But how viewers then decode and interpret that message is as variable and complex as humanity itself. The geographical context that informs an individual consumer’s identity influences the meaning of that message.
The imagery in Bond Films or stylized photos of Gu also don’t provide a voice to the displaced or marginalized people that make up the bulk of these ‘foreign’ populations. The West can use the power of imagery to impose meaning which only perpetuates the idea that the West controls the rest. ‘We’ hold dominion over ‘them’. As geographer Anoop Nayak puts it,
“The power of whiteness to continually narrate the existence of racialised Others is a violent reminder of the privilege that comes with being located as the architects and inheritors of modernity.”3

Eileen Gu just may be fashioning these Western media mechanisms into a weapon of her own. She has the potential to use her talent, intelligence, and good looks – and the dominant Western style media platforms – to give voice to those in China who do not. If we’re to believe Eileen Gu, she wants to inspire and empower young Chinese-born girls to use sport as a way to give them a voice.
She knows they don’t have Title Nine to help them in China, so she’s using her Chinese language skills and her individual beauty, elegance, intelligence, and grace as a substitute. All under a Chinese flag. She is using the media tools of traditional Western domination not to hush or misconstrue but to crush what oppresses young girls so they can see what they can do.
Eileen is outspoken and well spoken. She’s come out against increased Asian hate crime in America and supports the BLM movement. But she remains silent on human rights abuses in China. This really bothers people. Especially reporters.
Meanwhile Tesla sells more cars in China than anywhere in the world. Where are the calls for Elon Musk to speak out? Microsoft was the first software company allowed to open an office in China around the same time Eileen’s mom was coming to America. It remains a highly productive, innovative, and influential subsidiary for Microsoft. I’ve witnessed myself. I don’t see reporters demanding Satya Nadella or Bill Gates to come out against China. Eileen, just like Elon, Satya, and Bill, know that to do so means disadvantaging their chances for influence from inside China.
Could it be that these Western, mostly male, reporters only see Gu as a two-dimensional, bi-racial American girl? Are they put off by how she expertly and effortlessly dodges their questions? Are they frustrated they can’t dominate this woman, this girl, this Asian-American who can look and sound Western one moment and Chinese the next?
When the British reporter Oliver Brown writes how her well crafted and practiced line, “in the US, I’m American, and when I’m in China, I’m Chinese”, came across as ‘cute’ to him, is that not only condescending but patronizing, paternalistic, and misogynist? And did he not politicize, objectify, and perhaps ‘Orientalize’ her by insisting her words were “sadly impractical, for the simple reason that China does not recognise dual citizenship.”? There is nothing simple about any of this.
And am I guilty of doing the same when my first reaction was to judge her on her appearance without knowing anything about her, her life, her family, her culture, or her intentions?
Who knows what her real citizenship is. Maybe China turned a blind eye to their policy that refuses dual-citizenship. It’s a practical move on their part if it means they get a world renowned Snow Princess Chinese ambassador out of it. I wouldn’t put it passed Eileen and her mom to scheme and arrange such a deal. Her mom is a professional Chinese deal maker, after all. Just as Musk, Nadella, and Gates are. Who knows what arrangements these successful Western businessmen have with China, but you can bet they’re practical.
When the ski coach from Oregon – who knows a thing or two about dealing with Eileen and her mom – was pressed on what he thought of Eileen choosing to ski for China he said, “It’s a decision that seems practical and pragmatic, just like every decision she makes.”
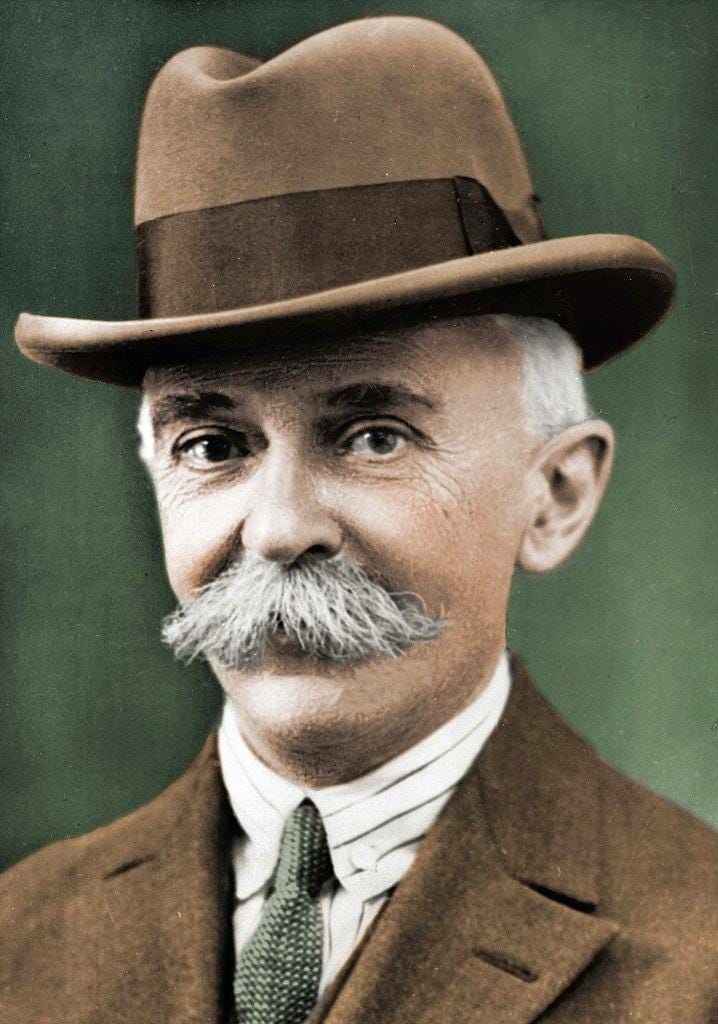
In the 1880s and 1890s, a French aristocrat interested in the history and sociology of sport toured America and England learning about sports administration. His name was Pierre de Coubertin. He was particularly fascinated by rugby. He believed it best demonstrated how “organised sport can create moral and social strength” and how it could “help to set the mind and body in equilibrium”. As a former rugby player, I concur.
He took his learnings back home and with the help of the French government organized the first Olympic committee in 1894. By 1896 the first modern Olympic games took place in Athens. It attracted the largest contingent of international athletes of the time.
As I watch the remainder of the Olympics I’m trying to see through the media veils that distort and disorient portrayals of people. Instead of being just another American rooting for Americans, I’m marveling at the athletically gifted, courageous, and tenacious humans participating in ‘organized sports that have shaped their moral strength.’
Maybe if we all do that together we can also build social strength. Watching Eileen Gu twirl through the air while dodging the admonishing stare can be dizzying — and then some. But seeing her as a human first and an athlete second sets my mind and body in equilibrium.
The Possibilities of Performance. Alan Latham, David Conradson. 2003.
Geographical Thought: An Introduction to Ideas in Human Geography. Anoop Nayak. 2015.
Ibid