Hello Interactors,
We are fully into spring and that means a shift toward cartography. I’ll be exploring how abstract symbols, lines, and colors can both represent and misrepresent people, politics, and the physical environment. Maps are tools of power and persuasion, which can shape perceptions of space and reality, influence behavior, and maintain or challenge social norms and power structures.
Today’s post bridges Winter’s focus on human behavior with the maps, plans, and politics of cities. In this case, Los Angeles and their attempts at curbing rising traffic related fatalities through safer forms of transportation infrastructure…but not without a fight from some unlikely foes.
Let’s go…
CURBSIDE CASUALTIES LEAD TO ASPHALT ACTIVISM
Angelinos recently passed a controversial measure intended to save lives. It won 63 percent in favor to 37 percent opposed. Maybe it wasn’t so controversial after all. Why should helping save children from being violently killed be controversial in the first place? And why were firefighters leading the charge to kill a measure that saves lives.
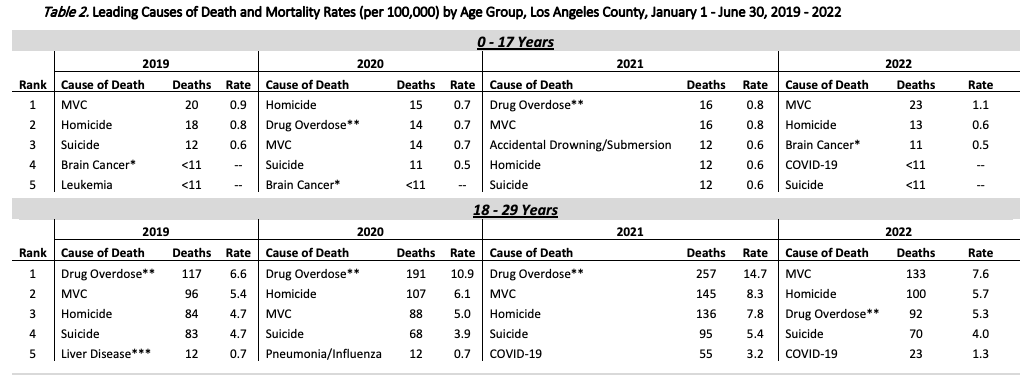
Car collisions were the leading cause of death for children in Los Angeles County in 2022. Drug overdose and homicide have been in competition with ‘motor vehicle collisions’ for the top kid-killer spot over the last few years. Drowning, another preventable killer my wife is focused on eradicating, was the number three killer in 2021.
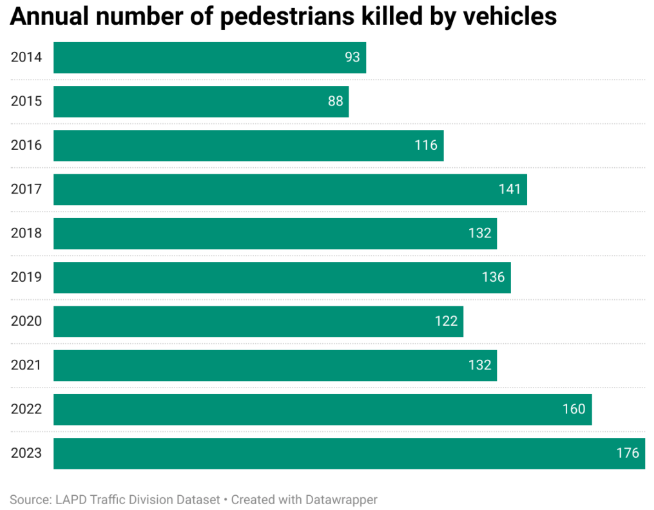
In January, the hyperlocal newsletter Crosstown reported data from the Los Angeles Police Department that 2023 was the “deadliest year on the roads in at least a decade, with 337 fatalities.”1
More than half of these were pedestrians. In 2022, 160 pedestrians died from being struck by a motor vehicle. It’s been getting worse for some time.
If you’re not already depressed, this might push you over the edge. Hit and runs are also climbing.
In October of 2022, the County of Los Angeles Public Health Department published the “Leading Causes of Death and Mortality Rates (per 100,000) by Age Group” in Los Angeles County from January to June for 2019 to 2022. During these years, of those aged 0-17, 73 have been killed by motor vehicles. In 2022, it was the number one killer.2
Alarmed by the trend, former Mayor Eric Garcetti formulated a “Mobility Plan 2035” in 2015 that “incorporates ‘complete streets’ principles and lays the policy foundation for how future generations of Angelenos interact with their streets.”3 This follows California state’s 2008 Complete Streets Act (AB 1358), which requires local jurisdictions to
“plan for a balanced, multimodal transportation network that meets the needs of all users of streets, roads, and highways, defined to include motorists, pedestrians, bicyclists, children, persons with disabilities, seniors, movers of commercial goods, and users of public transportation, in a manner that is suitable to the rural, suburban or urban context.”4
The rise in traffic deaths reveals that the aspirational goals set in various levels of government often represent legal fictions—idealized plans that simplify complex issues, but don’t always lead to action. These legal frameworks, while not intentionally misleading, can result in a disconnect between policy intentions and outcomes, promoting a status quo bias due to the complexities of change, systemic inertia, and established interests — including those of firefighters.
But a group of citizen activists organized to bring action to the fiction and gain traction amidst the friction. They drew attention to the fact that although L.A. had laid out a progressive ‘complete streets’ plan, they had only executed 5% since its inception nearly a decade ago. At that rate they calculated it would take 160 years to build a minimum network of safe streets. All the while hundreds upon thousands would die while the legal fiction would continued to paint a different picture.
So, they devised Measure HLA, the Healthy Streets L.A. initiative, inspired by other cities to bring action to ‘complete streets’ fiction. The measure states every time a street is resurfaced, any corresponding Network Mobility Plan improvements must be implemented. For example, if a street has been designated as a segment of a bike network and is due to be resurfaced, the city must install the protected bike lane (or other complete street infrastructure) needed to fulfill the city’s Mobility Plan 2050. Common sense exceptions are included to ensure public works could still fix things like potholes, utility cuts, or emergency repairs.
But installing 560 miles of pedestrian paths, 300 miles of enhanced transit lanes, 520 miles of bike lanes safe enough for an eight-year-old, 830 miles of neighborhood enhancements, and 800 miles of bike networks for all levels of cycling requires some sacrifices. Motorists will have to sacrifice space on roadways to accommodate these changes. In doing so many roads will be narrowed and speeds lowered thus sacrificing speed of vehicles.
And this is where the firefighters come in. There’s a common misperception among many firefighters and emergency responders that safe streets, that is slow streets, lead to slower response times resulting in people dying. The hundreds of people, including young people, they scrape off the pavement or extract from a car after being obliterated by a ton of metal charging at excessive speeds seem to be excluded from this calculus.
It is true there was a time when speed bumps were added to slow speeding vehicles that also slowed first responders. But civil engineers and urban planners worked through these challenges and now speed cushions can be installed that permit fire trucks (and other large vehicles) to proceed through gaps in the speed bumps. There are also ways to design safe street networks in ways that allow speeding emergency vehicles to move quickly through road networks protected from or free of pedestrians and cyclists…and clogged traffic. In many cases, it’s the same paths carved out of stalled traffic for buses.
FIRST RESPONSE AND EMERGENCY OBJECTIONS
The Los Angeles Fire Department (LAFD) seemingly haven’t gotten the memo from the Federal Highway Administration on how to calm traffic while not reducing response times. One LAFD Captain, Frank Lima, was quoted as saying “Firefighters are opposed to Measure HLA…[because] response times from 911 resources will increase…Every second in our profession means [life or death].”5 But Mr. Lima then exposes what is perhaps the true source of his opposition which is not related at all to his expertise or profession but likely a personal conviction.
“It’s going to hurt small businesses and it’s going to take away parking spaces,” he said. “It’s one of those projects that sounds good on paper, but when you put it in reality, it’s going to have a negative impact.”
He is right that legal fiction does sound good on paper, and on-street parking spaces may be taken away on some streets, but if done well other cities have shown small business improves as does property value. It turns out everybody wants to live on a safe and quiet street, expect maybe this LAFD Captain.
Mr. Lima is also a member of the International Association of Firefighters and presumably the United Firefighters of Los Angeles City Local 112 (UFLAC) who claim they spent $100,000 fighting this measure. Their president, Freddy Escobar, said Measure HLA “is full of lies…all these confusing lanes, dangerous bike lanes, pedestrian medians, and all the chaos - and nobody is using 'em."6 If that was extreme enough in his attempt to scare voters, he added, “If we pass HLA we're going to see chaos all over the city.”
Not to be out done, the president of the California Professional Firefighters, Brian Rice, also revealed his personal convictions while presumably speaking on behalf of all California firefighters stating,
"I hate to tell you men and women, California - and Los Angeles in particular - this is a car community. You may not like it, but it is."
He then took a shot at bus drivers and riders who are stuck in traffic today but will benefit from bus priority signaling and bus only lanes as part of the complete streets plan. He asked,
"Do you really think you're going to see buses go faster than 12 miles an hour?"
And then, he fully exposed his motivations for wanting to deny Angelinos safe streets. Dog whistling conservatives across L.A., he claimed the initiative came from “a small group of elite...Democratic Socialists.”
It might seem unusual for firefighters to be so misaligned with most people they serve (the measure passed by a 2 to 1 margin) or for their personal convictions or biases to seemingly conflict with their egalitarian duty to serve all members of the community, but it’s not.
Firefighters are unique. They’re the only profession that attracts people who need to be trained NOT to immediately run into a burning building. As one fire chief said to his trainees,
“Risk a lot to save a lot. Risk a little to save a little. Risk nothing to save nothing. We’re all here to help people... but you need to have your priorities straight: life safety first, incident stabilization second, and property conservation last.”7
These people must not only endure and survive extreme physical conditions, but they are also exposed to human pain and suffering, mutilations, and death. All of which require a healthy support network and relationships to maintain their mental health. This is why their training and work environment also includes indoctrination an institutional culture that instills comradeship, respect, and devotion to service — for each other and the communities they serve.
But within any group of people each individual member shows up with their own implicit or explicit biases toward minority members of any community they may serve, be it class, race, ethnicity, gender, or apparently pedestrians, cyclists, transit riders, and those with opposing political views. How might these biases interfere with their duty to serve all community members?
Much of our behavior is subtly influenced by unconscious biases, deep-seated preferences we're often unaware of. These hidden biases can significantly impact daily decisions and societal dynamics, especially in critical areas like healthcare, where they contribute to disparities in patient treatment and outcomes.
Similarly, in the criminal justice system, implicit biases affect law enforcement actions, with studies indicating varying responses based on race. However, the connection between these unconscious biases and actual discriminatory behavior remains a topic of debate, with some research suggesting the link is weaker than previously thought, emphasizing the complexity of addressing such ingrained biases.
One researcher embedded himself in a fire crew in a small town in the southern United States to explore these complex behaviors. To be accepted as ‘one of the guys’ the researcher went through training and served on calls with the crew. It took weeks, but he eventually earned his insider status where he felt everyone was acting normally should he not be observing them. It wasn’t pretty.
AMIDST FLAMES OF PREJUDICE, A BROTHERHOOD IN THE BALANCE
As a member of a white crew serving a racially and ethnically diverse community, he indeed uncovered some alarming and explicit individual biases. In a banter of stories about various calls, he observed a trend in one-upmanship among story tellers. “Tall tales” is a form of bonding among groups of humans that have existed across time and culture. Each story becomes increasingly exaggerated and in the case of the culture of this group of firefighters, explicitly racist, sexist, and/or classist. One such crescendo culminated with this alarming tale (trigger warning, some nasty and disturbing language in here),
“Green Village is the worst because you’ve got all those Mexicans who don’t fucking speak English. At least at Friendship Haven, you can say, ‘Listen, bro, I’m gonna call the fucking cops,’ and they scurry off. [He simulates running, while holding up pants] These fucking Mexicans don’t speak English, so they’re a pain in the ass. Those Jose Cuervos think they are doctors. There was that one call at Green Village, where there was this woman. It was toned out [dispatched] as a cardiac arrest, but we got there and the woman was having a seizure.
Anyway, it was me and Kelly and we pulled her out of the bed to this little spot on the floor between the bed and dresser and her two sons were like standing over her. One was flashing a light in her face, like a flashlight. And she was fat, obviously. And the other one was pulling her shirt down to cover up her fat, while yelling, “She dead. She dead.” The woman was fine. I walked out and called police on that fucking Beaner. If I would have had a gun, I would have shot those two Speedy Gonzalezes.”
In another story, a Black woman in a hijab arrived at a residence where the crew was cleaning up after a call. Laughing, one of the firefighters asked his crew,
“Did you see what they were cooking? There were bones in that pot.” His colleague responded, “What was it? A cat? Rats? Hamsters?”
Amidst the laughter another story was shared.
“Remember we were at that fire last weekend, over in Africa, and that woman slapped the shit out of that guy?” One of the Lieutenants replied how hilarious it was while stomping his foot performing a racist caricature and mimicking an African language saying “…she was yelling and really going off on him in Black.”
Upon hearing this, the researcher reported, one of the firefighters laughed so hard he lost his breath. As the laughter subsided another firefighter said of the neighborhood they were serving, “Friendship Haven can burn down and I wouldn’t give a fuck. Fuck. That. Hellhole.”
It’s hard to read this and imagine why these bigoted firefighters bother even showing up to help these people. But according to the researcher, this is how a fraction of these “white, male, working-class firefighters cope with stress and forge solidarity” while most of the others passively laugh and follow along.
He claims these individual beliefs don’t interfere with their duty to serve because the one thing that would exclude a firefighter from the ‘brotherhood’ is allowing a human to suffer or die — regardless of how they may personally feel about them. He said that while this Southern white “working-class, locally raised, politically conservative peer culture dominates the social space…prejudiced beliefs take a back seat to enacting excellence on the fireground.”
He says because these extremely discriminatory words and actions are portrayed in private and only among other firefighters they entrust, and issued by those in command, there is little opportunity for disciplinary action. He also believes “it is a tall order to exorcise prejudice from individuals.” The best remedy to counter these individual beliefs, the researcher writes, is to start by “educating staff about the populations they serve and teaching nonviolent approaches to conflict resolution.” He also believes “organizational incentives that encourage grassroots competition to provide optimal service or community engagement can stymie discriminatory behavior.”
In the case of the LA firefighters, they are clearly more ethnically and racially diverse than those this researcher observed in the South, so attacks on minority races is unlikely happening in the open. And what discriminatory prejudices these L.A. firefighters do have are clearly not just private. After all, they just spent $100,000 to make them public.
Should a social psychological researcher embed themselves in any number of these L.A. squads, I’m sure they’d reveal disparaging language there too. Their quasi-militaristic allegiance to the ‘brotherhood’ is evidently forged in a shared disdain for ‘cyclists’, ‘pedestrians’, liberal ‘elite social democrats’, and/or some ‘others’ outside their tribe.
As for those firefighters who may be partial to, or members of, these ‘other’ tribes, and perhaps even chided for being one of ‘them’, the group likely accepts them because even if they’re a negatively branded a ‘liberal socialist’ they’d still risk their life to save another crew member or community member.
American firefighters are portrayed as heroes in America. Movies like Backdraft or television shows like 9-1-1 portray firefighters as tough, rugged, fearless public saviors. The heroic narrative can attract those seeking action, adventure, and camaraderie awash in a glamorous glow of danger. But perhaps society’s hero worship can also insulate those with hateful and bigoted views from public scrutiny. They will perform heroic acts to society’s benefit, but perhaps with a bit more education, less bravado, and more tolerance they could become better firefighters and heroes.
One veteran of emergency services, fire marshal, and U.S. Marine Desert Storm war veteran, Daniel Byne, made a plea in 2007 to,
“Take off the macho T-shirts. Take down the pictures and posters that paint our profession in an unrealistic light and encourage our firefighters to take unwarranted chances in the pursuit of living up to an unrealistic image.”8
He is echoing criticisms from a Swedish firefighter Dr. Stefan Svensson, a PhD in fire engineering. He says in many countries the ‘heroic deeds’ many American firefighters are lauded for “would probably had led to inquiries, changes in training manuals, the dismissal of the fire fighter and probably even prosecution of the fire fighter for causing immediate danger to others.” Perhaps the bigoted attitudes may also.
Curiously, some of these other countries happen to be social democracies like Sweden. After this country of nearly 10 million people instituted similar ‘complete streets’ initiatives in 1997, their pedestrian deaths dropped from 134 in 1990 to 25 in 2020. Sweden and Norway have the smallest numbers of traffic related deaths per 100,000 inhabitants in the world, thanks to Vision Zero and ‘complete streets’ initiatives.
Sweden’s Svensson’s message for American firefighters is this:
“Bravery and heroic deeds must result from knowledge, not from illusions.”9
Perhaps it’s time more firefighters get educated on the negative effects of outwardly expressing hatred toward others, trust their fellow public service colleagues like city planners and engineers, and learn to operate their equipment on streets designed for all — even if that means learning it from people they disparage as ‘social democrats.’ After all, as that fire chief in the South said, “We’re all here to help people... but you need to have your priorities straight.”
Another awful year on Los Angeles streets, with 337 traffic deaths. Crosstown. LA by the numbers. Jon Regardie. January 2024.
Patterns in Mortality Among Los Angeles County Residents from January 1 – June 30 of 2019, 2020, 2021, and 2022. Office of Health Assessment and Epidemiology: County of Los Angeles Public Health. October 20, 2022; Updated November 10, 2022.
Mobility Plan 2035 : An Element of the General Plan. Los Angeles Department of City Planning. Adopted by City Council: September 7, 2016.
California Assembly Bill No. 1358 : CHAPTER 657 (AKA 2008 Complete Streets Act). Signed into law by California Governor Arnold Schwarzenegger. Effective 2011.
Los Angeles firefighters oppose street modification measure. KTLA. Will Conybeare, Ellina Abovian. February 2024.
Firefighters Oppose L.A. City Safe Streets Initiative Measure HLA. StreetsBlog LA. February 2024.
Risk a Lot to Save a Lot: How Firefighters Decide Whose Life Matters. Roscoe C. Scarborough. Sociological Forum, Vol. 32, No. S1. December 2017.
Hero Complex: It Can be a Good Thing. Dan Byrne. Fire Engineering. 2007.
Reducing fire fighter fatalities – the knowledge based approach. Dr. Stefan Svensson. Presented as a public service of the Public Entity Risk Institute (PERI). 2